10 Business Opportunities To Dominate And Make Competition Surrender
Discover how to identify and leverage your startup's unfair advantage to dominate the market. This guide explores powerful strategies and real-world examples to inspire entrepreneurs aiming for success—essential reading for innovative business leaders.

In the fiercely competitive landscape of entrepreneurship, standing out is not just an option—it's a necessity. The Lean Business Canvas teaches us the importance of identifying our "unfair advantage," a unique edge that sets us apart and ensures our business enters and dominates the market. An unfair advantage is that ace up your sleeve that competitors can't easily replicate or buy. Let's delve into what makes an unfair advantage so powerful and how to leverage it to secure your position in the market.
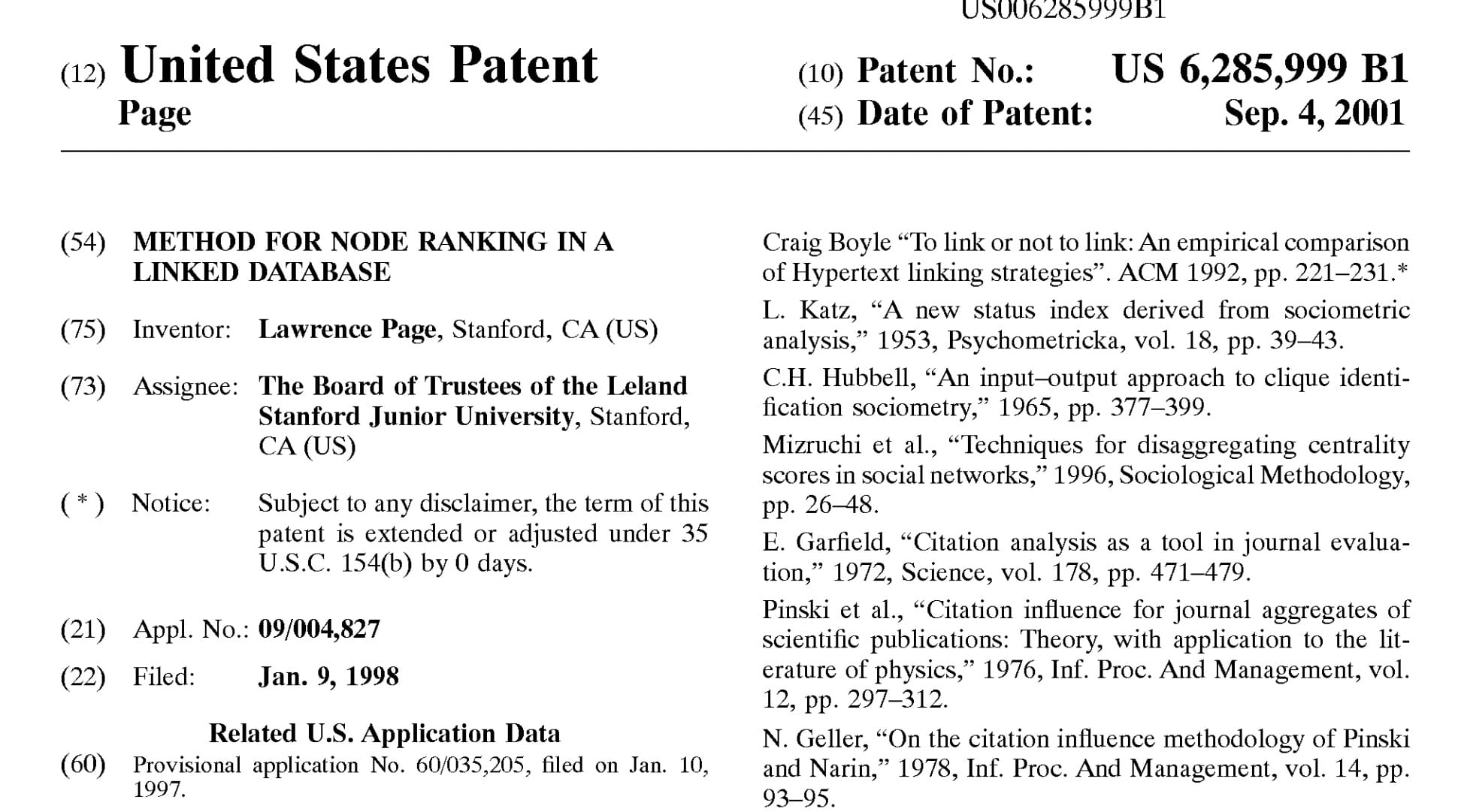
1. Proprietary Technology or Patents
Innovation is the cornerstone of competitive advantage. You're holding a golden ticket if your business has developed proprietary technology or secured patents. This could range from a groundbreaking software algorithm to an innovative manufacturing process. The key here is exclusivity—technology only you can offer to the market.
- Example: Google's Search Algorithm - Google's proprietary search algorithm is a prime example of how patented technology can be a decisive unfair advantage. It has continually evolved, making it difficult for competitors to match Google's search accuracy and speed.

2. Exclusive Partnerships or Licenses
Imagine having a key that opens doors no one else can even approach. Exclusive partnerships or licenses act as this key, providing you with resources, distribution networks, or products that are off-limits to your competitors. Whether it’s exclusive selling rights in a lucrative market or access to cutting-edge technology, these partnerships can drastically elevate your market position.
- Example: Netflix and Disney Content Partnership - Before Disney+ was launched, Netflix's exclusive partnership to stream Disney movies was a significant unfair advantage, drawing in millions of subscribers who wanted access to Disney's library.

3. Brand Recognition and Customer Loyalty
Never underestimate the power of a strong brand. Brand recognition and customer loyalty are earned through consistent quality and trust-building. This advantage is a fortress; it's formidable and time-consuming for competitors to breach. A loyal customer base not only provides a steady revenue stream but also serves as a formidable barrier to new entrants.
- Example: Apple's Brand Loyalty - Apple has cultivated immense brand loyalty among consumers, with a reputation for innovation, quality, and a seamless ecosystem of products and services, making its customers highly likely to repurchase Apple products.

4. Network Effects
The more, the merrier—this principle underlies the network effects. Each new user enhances the value of your product or service for others, creating a self-reinforcing growth cycle. Platforms like social media or marketplaces, where the user experience improves as more people participate, can quickly outpace competition once critical mass is achieved.
- For example, Facebook's user base grew exponentially due to network effects. Each new user made the platform more valuable for others by increasing potential connections and interactions, solidifying its position as the leading social network.

5. Cost Advantage
Dominating the market isn't always about having the flashiest product; sometimes, it's about offering the best value. A cost advantage means you can provide competitive pricing while enjoying healthy margins, thanks to economies of scale, efficient processes, or unique access to cost-effective resources.
- Example: Walmart's Supply Chain Efficiency - Walmart has built a robust supply chain that consistently offers lower prices than competitors. This cost advantage has been central to Walmart's strategy, attracting price-sensitive customers and maintaining market leadership.

6. Talented Team
The brain behind the operation is your most valuable asset. A team of skilled, innovative professionals can execute and innovate at levels that leave competitors in the dust. This includes everyone from visionary leaders to expert developers who can pivot and adapt faster than others in the market.
- Example: SpaceX - SpaceX's innovation in the aerospace industry is driven by its team of top engineers and the visionary leadership of Elon Musk. Their ability to innovate and execute complex projects has made SpaceX a leader in space exploration.

7. Unique Business Model
Disruption is the name of the game. A unique business model can redefine an industry, creating a new standard that others struggle to match. Whether through a subscription service in a traditionally single-purchase industry or a novel platform connecting users in unprecedented ways, being different—and better—can make all the difference.
- Example: Uber's Ride-Sharing Model - Uber disrupted the traditional taxi service industry with its innovative platform that connects drivers with passengers directly through an app, offering convenience, competitive pricing, and a seamless user experience.
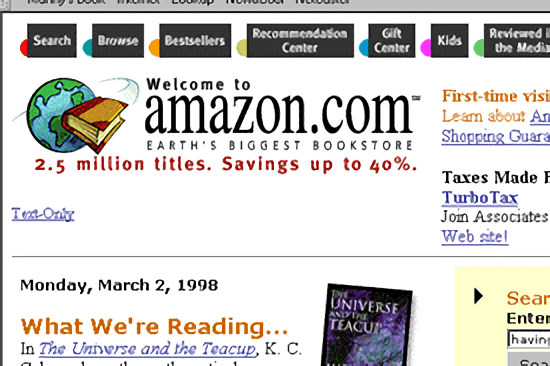
8. First-Mover Advantage
Sometimes, timing is everything. Being first to market can give you a temporary monopoly, allowing you to set the tone, establish brand recognition, and build customer relationships well before anyone else enters the race.
- Example: Amazon's E-commerce Platform - Amazon was one of the first companies to sell books online, quickly expanding into various products. This first-mover advantage allowed it to establish a dominant e-commerce platform early on.
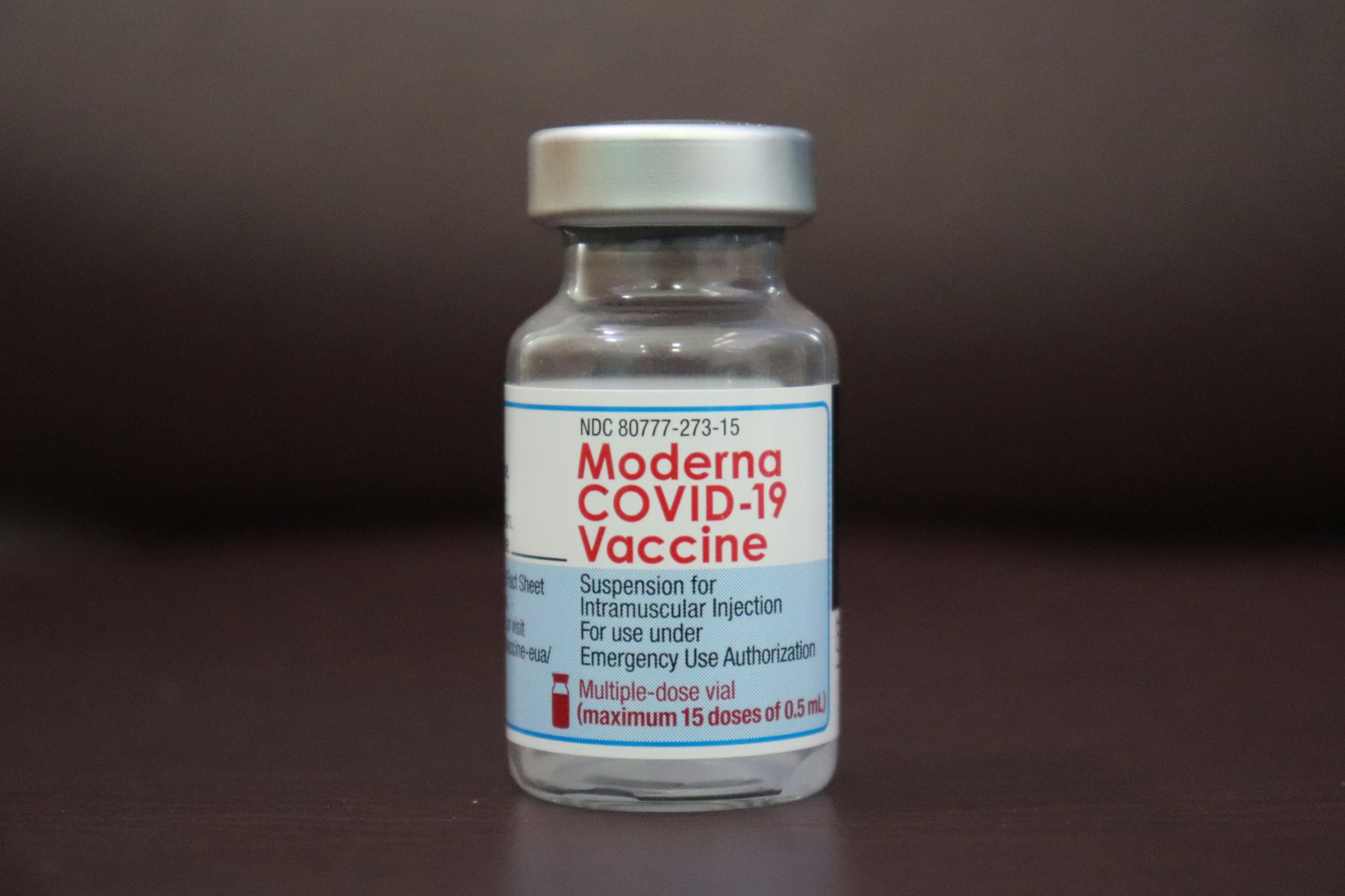
9. Regulatory Approval
Securing approval can be akin to having an exclusive pass in industries where regulation is a significant barrier. This is especially true in the pharmaceuticals, biotechnology, and finance sectors, where the approval process can be lengthy and complex.
- Example: Moderna and COVID-19 Vaccine - Moderna's rapid development and approval of a COVID-19 vaccine gave it a significant market advantage, allowing it to capture a large share of the vaccine market.

10. Access to Scarce Resources
Having something that everyone wants but no one else can get is a surefire way to ensure demand. Exclusive access to scarce resources, tangible or intangible, can provide a competitive edge that is hard to beat.
- Example: De Beers and the Diamond Market - For decades, De Beers controlled a significant portion of the world's diamond supply, effectively managing market availability and diamond prices and illustrating the power of access to scarce resources.
In Conclusion
Your unfair advantage is your secret weapon. It’s what makes your business uniquely capable of confidently tackling the market. But remember, resting on your laurels is not an option. The market is dynamic, and what gives you an edge today might not be as effective tomorrow. Continuous innovation, staying in tune with your customers’ evolving needs, and always being ready to pivot are essential strategies to maintain your advantage.
To all entrepreneurs out there: identify, nurture, and leverage your unfair advantage. It's not just about entering the market; it's about owning it.
Suggested Reading
To further inspire your journey and deepen your understanding of building a sustainable competitive edge, consider adding the following books to your reading list:
- "The Lean Startup: How Today's Entrepreneurs Use Continuous Innovation to Create Radically Successful Businesses" by Eric Ries - This book introduces the lean startup methodology, emphasizing the importance of agility, rapid prototyping, and validated learning. It's a must-read for entrepreneurs looking to build sustainable businesses in today's fast-paced world.
- "Zero to One: Notes on Startups, or How to Build the Future" by Peter Thiel with Blake Masters - Thiel, a renowned entrepreneur and investor, shares his insights on creating a successful startup. The book focuses on going from zero to one, creating new and unique businesses that offer unprecedented value.
- "Blue Ocean Strategy: How to Create Uncontested Market Space and Make the Competition Irrelevant" by W. Chan Kim and Renée Mauborgne - This book presents the blue ocean strategy, a revolutionary approach to business strategy that focuses on creating new market spaces (blue oceans) rather than competing in existing markets (red oceans). It offers practical frameworks and tools to help entrepreneurs find and exploit uncontested market spaces.
Each book provides unique perspectives and actionable strategies to help entrepreneurs understand and leverage their unfair advantages, navigate the complexities of startup growth, and achieve lasting success in their ventures.

